Various poisons and how to provide first aid for them
- CareBuddy
- 4 Mins Read
- 21 Sep 2022
- First Aid & CPR

Poisoning takes place when a toxic substance enters the body in one way or another and causes injury or death.
Common poisons include
- Carbon monoxide (e.g. from car engines and burning stoves)
- Drugs (including medication in excessive doses)
- Industrial waste
- Cleaning products and detergents
- Pesticides and bug spray
- Food that’s spoiled or the person is allergic to
- Fertilizers, herbicides and fungicides
- Metals such as lead and mercury
- Certain types of mushrooms and plants like poison ivy
- Venom from animal bites and insect stings
Symptoms of poisoning include
- Nausea and vomiting
- Breathing difficulty
- Seizures
- Dizziness
- Headache, giddiness or confusion
- Faster heart rate and palpitations
- Loss of consciousness
- Presence of poisonous substances nearby
- History of substance abuse (e.g. puncture marks on skin)
Poison may enter the body through
- The mouth (ingestion)
- The lungs (inhalation)
- The skin (absorption)
- Bites or stings (injection)
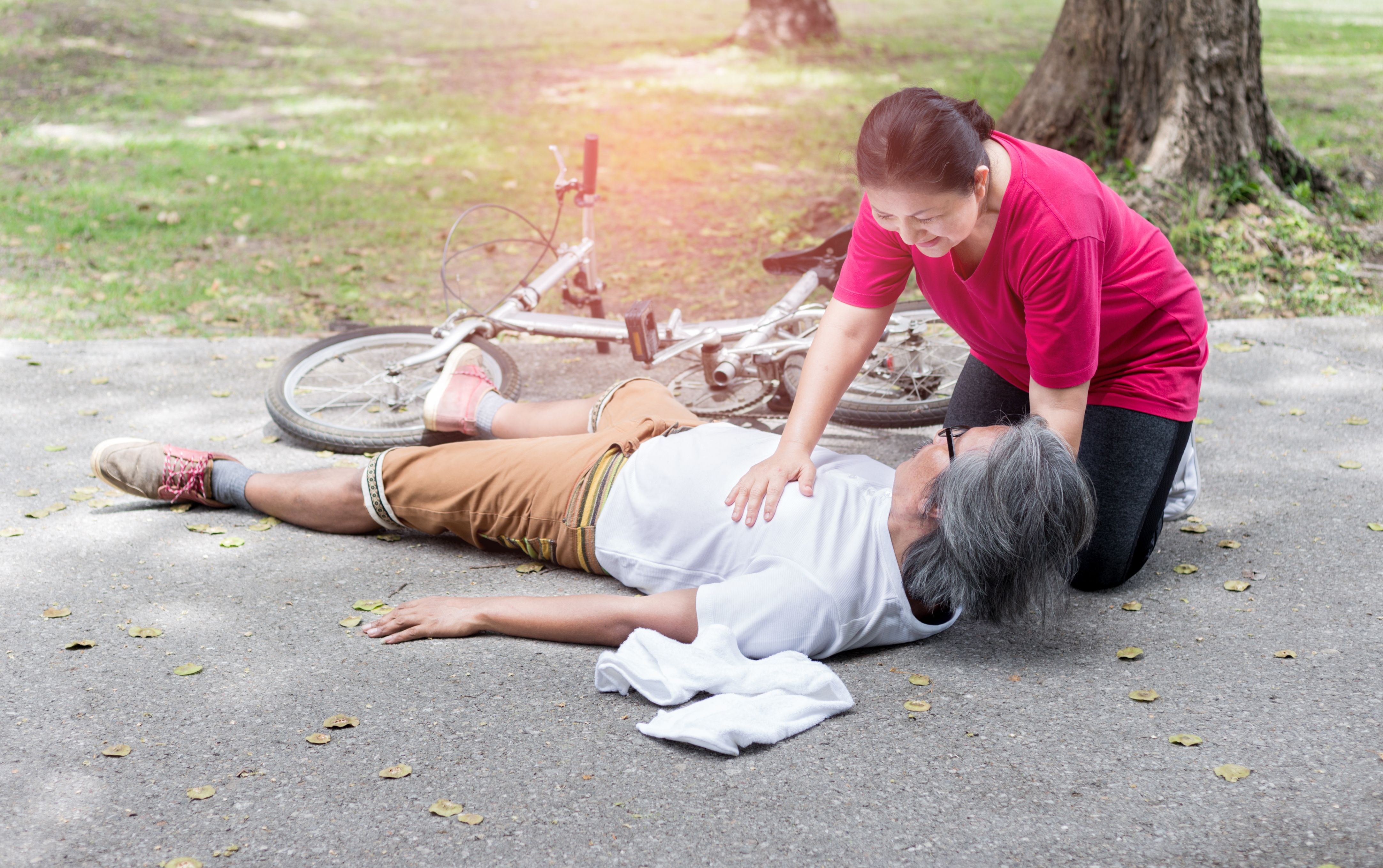
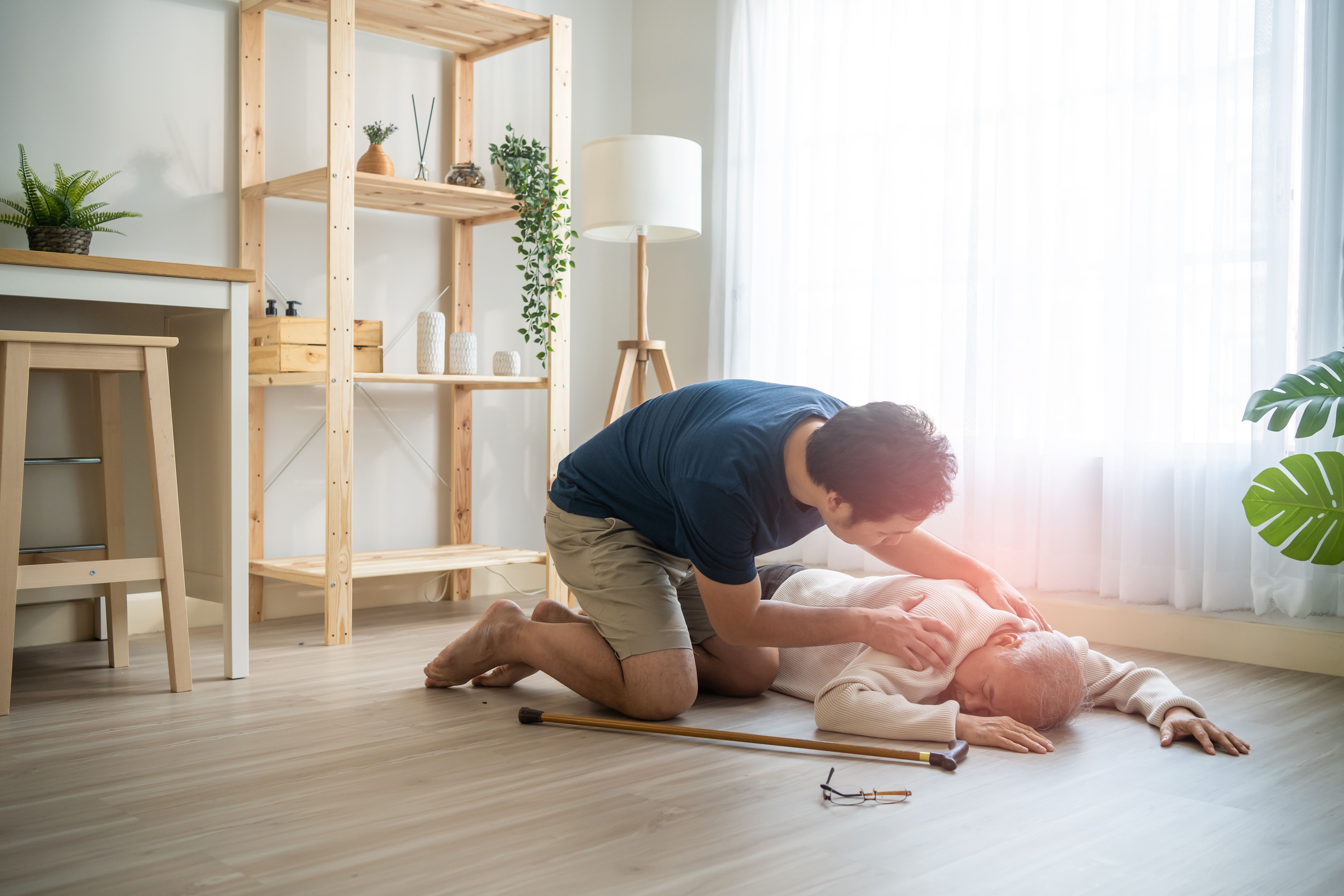
First aid for poisoning
- Remove the person’s exposure to the toxic substance as soon as possible. This may involve washing it off them (if it’s a substance on their skin or eyes) or removing contaminated clothing and jewelry (if the substance has spilled on those items) or moving the affected person away from the environment and into fresh air (if it’s toxic fumes in the atmosphere)
- If they are conscious, ask them to spit out anything they may have swallowed (if it’s poisoning via ingestion). But that’s only if the poison is still in their mouth. Don’t force them to vomit unless it is a natural body reaction
- Call 995 for emergency medical services
- Do not leave the person unattended at any time.
- Don’t force them to drink more water unless advised by a doctor or a paramedic.
- (Bring this to the top) If they are unconscious and not breathing), Commence Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR. Find out more about CPR at [Link to our CPR article]
- Ensure personal safety when handling the substance.
- Provide the doctors and paramedics with a summary of what happened, including any information about the poison that’s available (e.g. medication bottles or half-eaten food found at the site of the poisoning)
Treatment for poisoning
Doctors will identify the poison used so that they’ll prescribe the appropriate treatment such as an antidote. The bystander’s role in providing as much information as possible will be crucial to this.
Preventing poisoning
The best thing would be if there’s no poisoning in the first place. Possible ways to prevent poisoning include
- Ensuring that drugs and medication are clearly labeled and only accessible to those who’ve been prescribed the medication. Keep them out of the reach of children.
- Knowing what the person is allergic to (e.g. specific food or gases) and removing those substances from their day-to-day environment.
- Using carbon monoxide detectors to know when the carbon monoxide at a location is exceeding healthy levels.
Article reviewed by David Tay, Senior Principal Educator (Nursing and Prehospital Care), HMI Institute.