First aid for shock and bleeding
- CareBuddy
- 4 Mins Read
- 21 Sep 2022
- First Aid & CPR
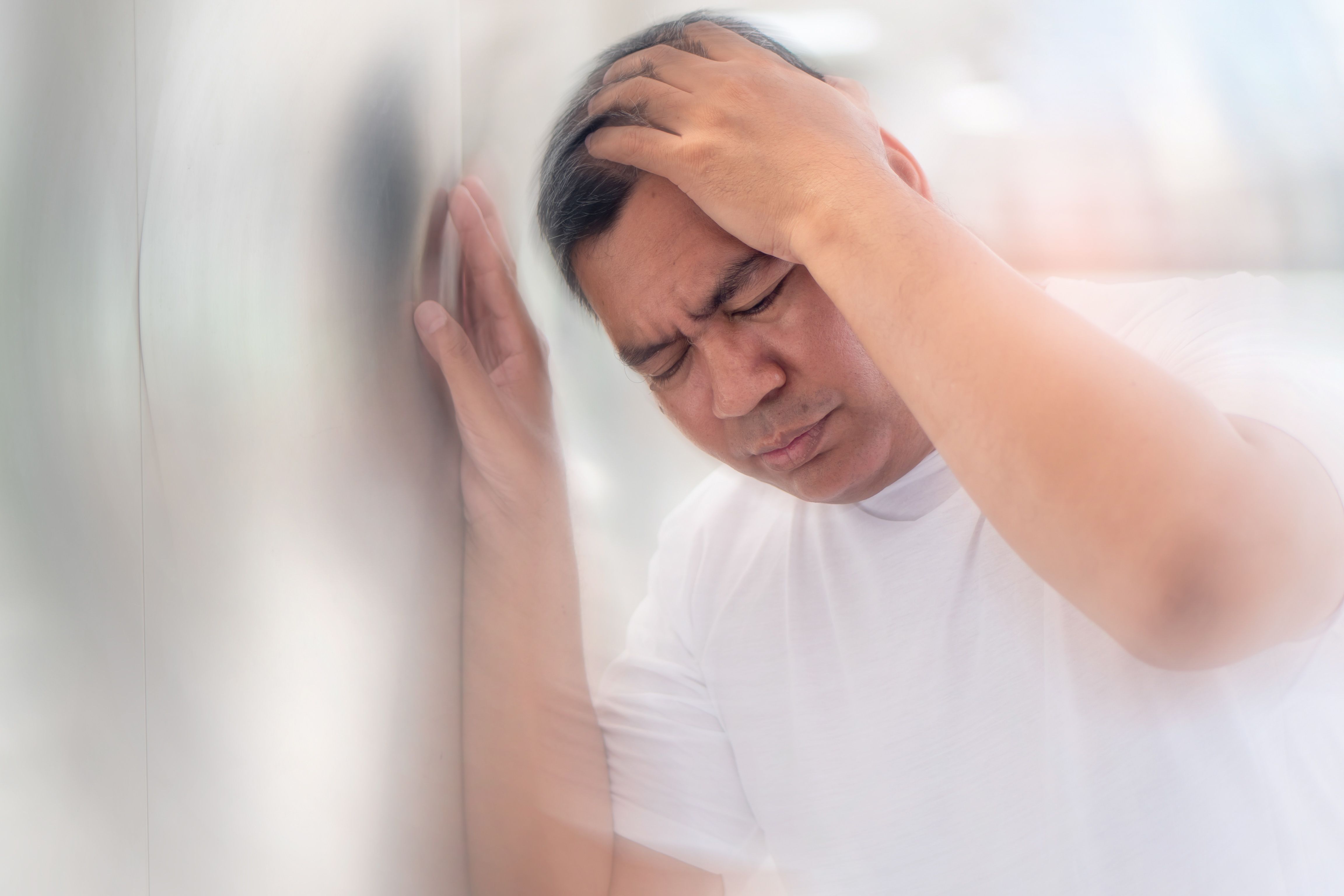

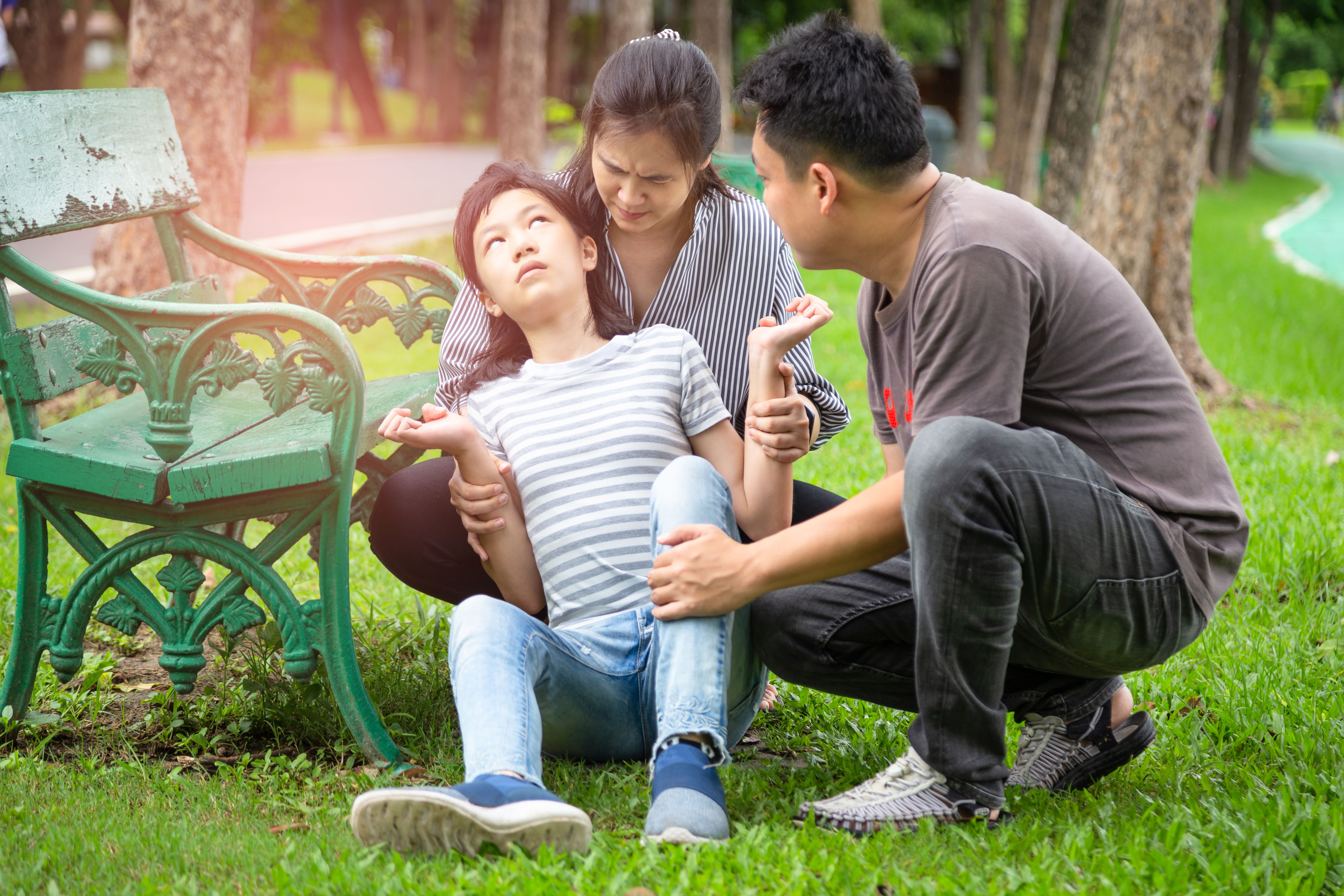
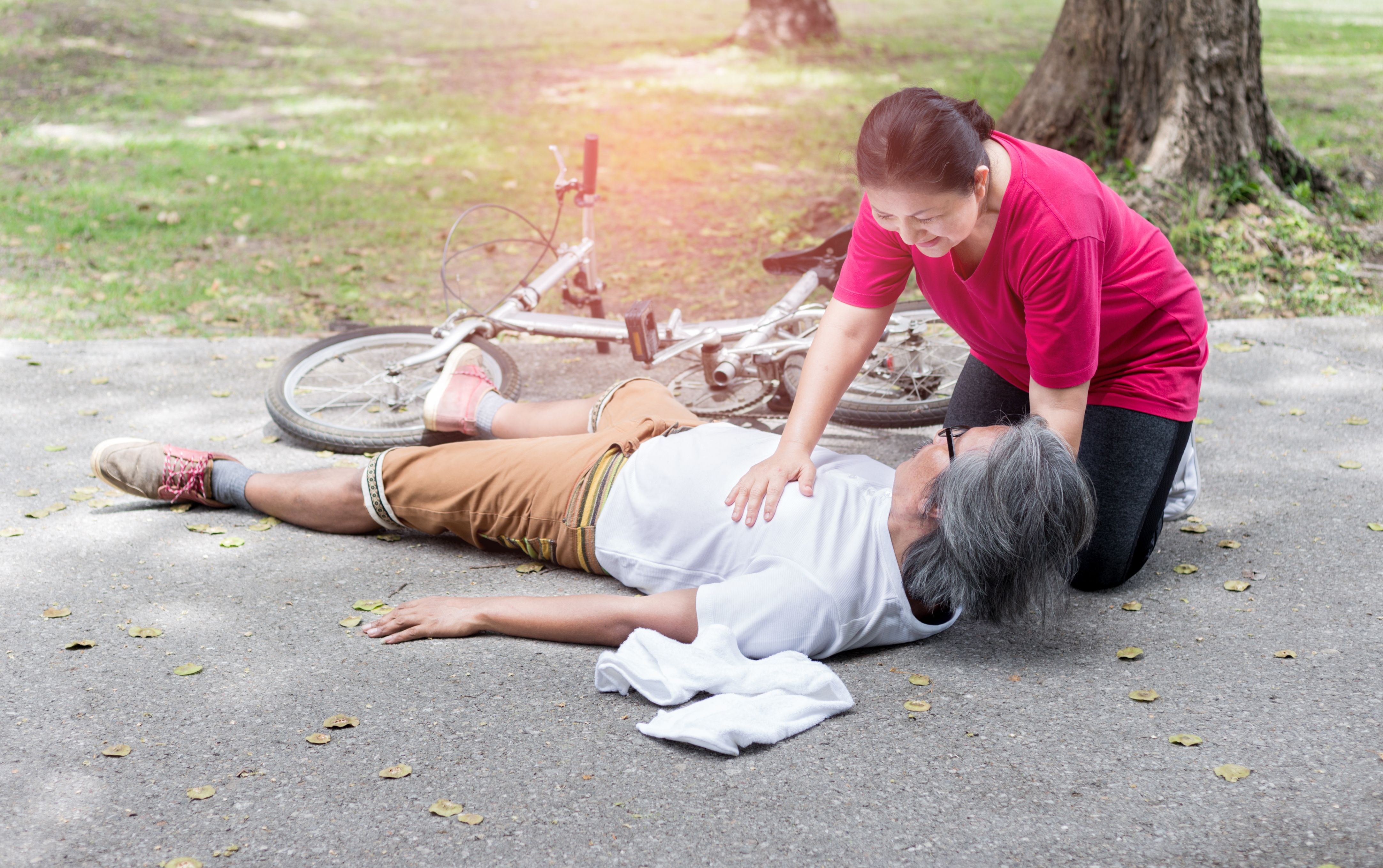
Shock is a sudden loss of blood circulation that can lead to organ damage and eventually death. Not to be confused with emotional shock, this is purely to do with blood circulation. Insufficient blood circulation means there’s inadequate oxygen delivery at a cellular level, which is why many different organs can fail in the event of shock.
Types and causes of shock
Cardiogenic shock: When the heart cannot pump enough blood and oxygen to the brain and other vital organs
Hypovolemic shock: The body is dehydrated due to severe blood or other fluid loss (this is the most common type of shock)
Anaphylactic shock: Due to a severe allergic reaction within the body
Signs and symptoms of shock include
- Skin temperature - Cool and clammy
- (Skin colour) - Bluish and pale
- Drowsiness
- Increased heartbeat
- Rapid and shallow breathing
- Anxiety
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Dizziness
First aid for shock
1) Call 995 for emergency medical services.
2) Arrest bleeding
3) Help the person rest by placing them in shock position. Lie flat with legs elevated.
4) Loosen any tight clothing.
5) Keep the care receiver comfortable and reassure them.
6) Do not leave the care receiver unattended at any time.
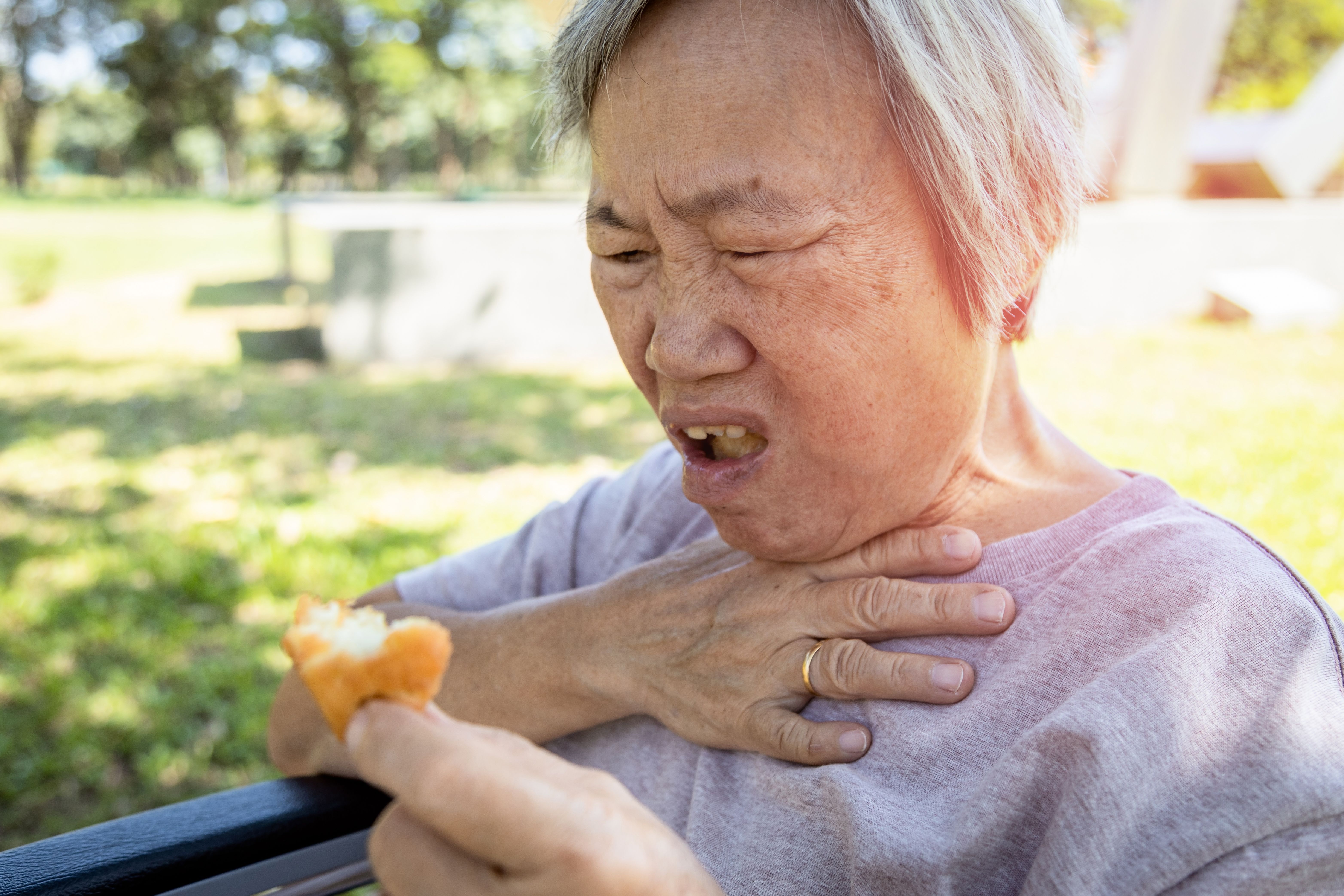
Hemorrhage (bleeding) and its relationship with shock
Hemorrhage is bleeding that takes place due to blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. It can occur internally, or externally through either a wound in the skin or a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus. This is one of the common causes of shock.
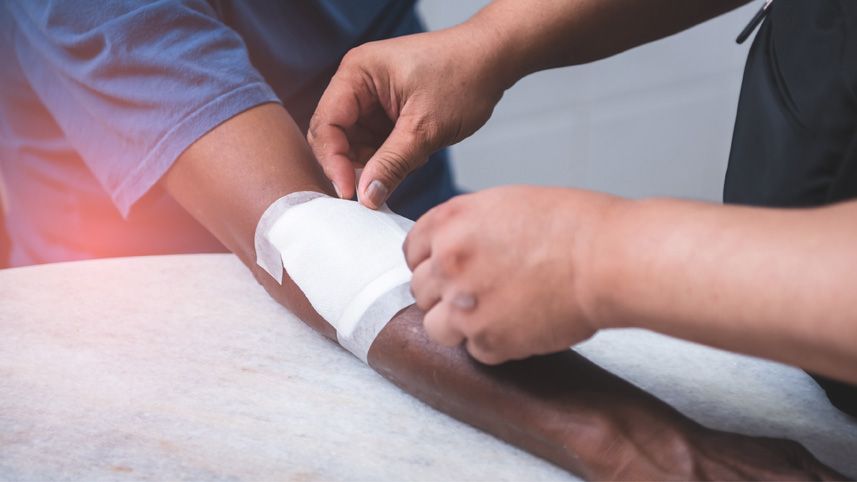
First aid for hemorrhage
- Apply direct pressure to the wound using a gloved hand and a clean dressing.
- Apply pressure bandage with a bulky gauze pad over and beyond the edges of the wound and bandage firmly. If bleeding continues, add another gauze pad and bandage firmly over the primary pressure dressing.
- Do not disturb the pressure dressing(s) once bleeding is controlled.
Article reviewed by David Tay, Senior Principal Educator (Nursing and Prehospital Care), HMI Institute.