Allergic reactions and how to cope with them
- CareBuddy
- 4 Mins Read
- 20 Sep 2022
- Respiratory Diseases
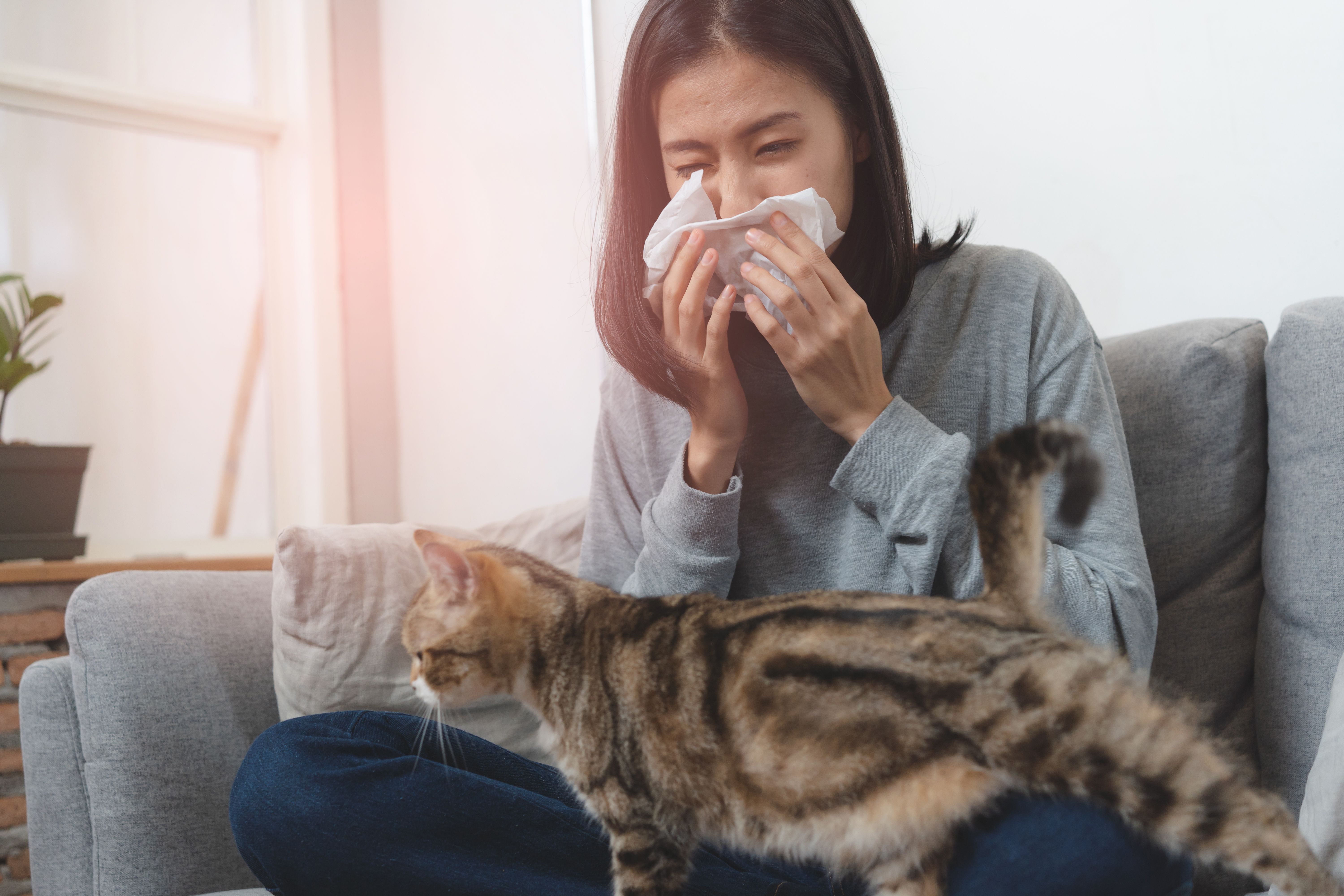

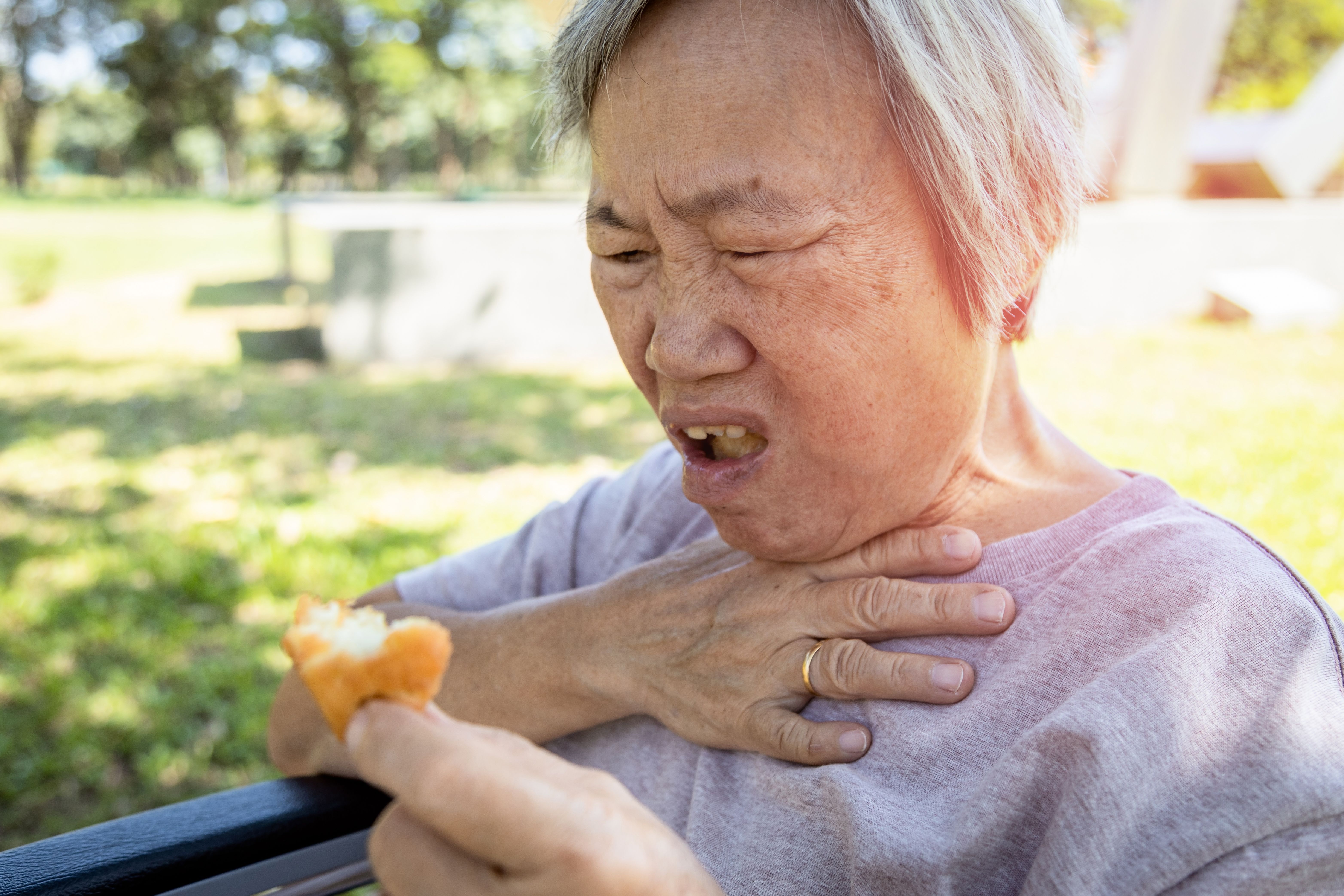
Many people have allergies to a variety of substances. Some of them can be commonly found in their environment or common foods, so they need to be careful to avoid those substances. Their reactions to these substances can be a minor nuisance or they could even be life-threatening. A severe life-threatening allergy is known as anaphylaxis.
What causes allergies
Our immune system has evolved to protect us from harmful substances. But sometimes, the immune system mistakes a harmless substance as a harmful one and reacts to it as if it were harmful. Ironically, the immune system’s reactions become more harmful than the substance itself.
Common allergy triggers
Food:
- Peanuts
- Tree nuts
- Shellfish
- Eggs
- Wheat
- Soy
- Milk
- Fish
Environment:
- Pollen
- Dust mites
- Mould
- Grass
- Animal dander
- Household chemicals
Others:
- Certain types of medicines
- Insect bites and stings
- Latex (e.g. in gloves and condoms)
Symptoms of allergic reactions
While not everyone will have every symptom, here are the most common symptoms of severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis).
Skin symptoms (reported in 80-90% of cases)
- Pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Flushing
- Itch
- Hives
Respiratory symptoms (reported in 70% of the cases)
- Cough
- Pain or difficulty swallowing
- Hoarse voice
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
Gastrointestinal symptoms (reported in 30-45% of the cases)
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Cramps
Cardiovascular symptoms (reported in 10-45% of the cases)
- Low blood pressure leading to giddiness
- Abnormal heart rate
Central Nervous System symptoms (reported in 10-15% of the cases)
- Headache
- Anxiety
- Confusion
- Lightheadedness
Others
- Watery eyes
- Loss of consciousness
- Runny nose
- Swelling of lips, tongue and/or throat
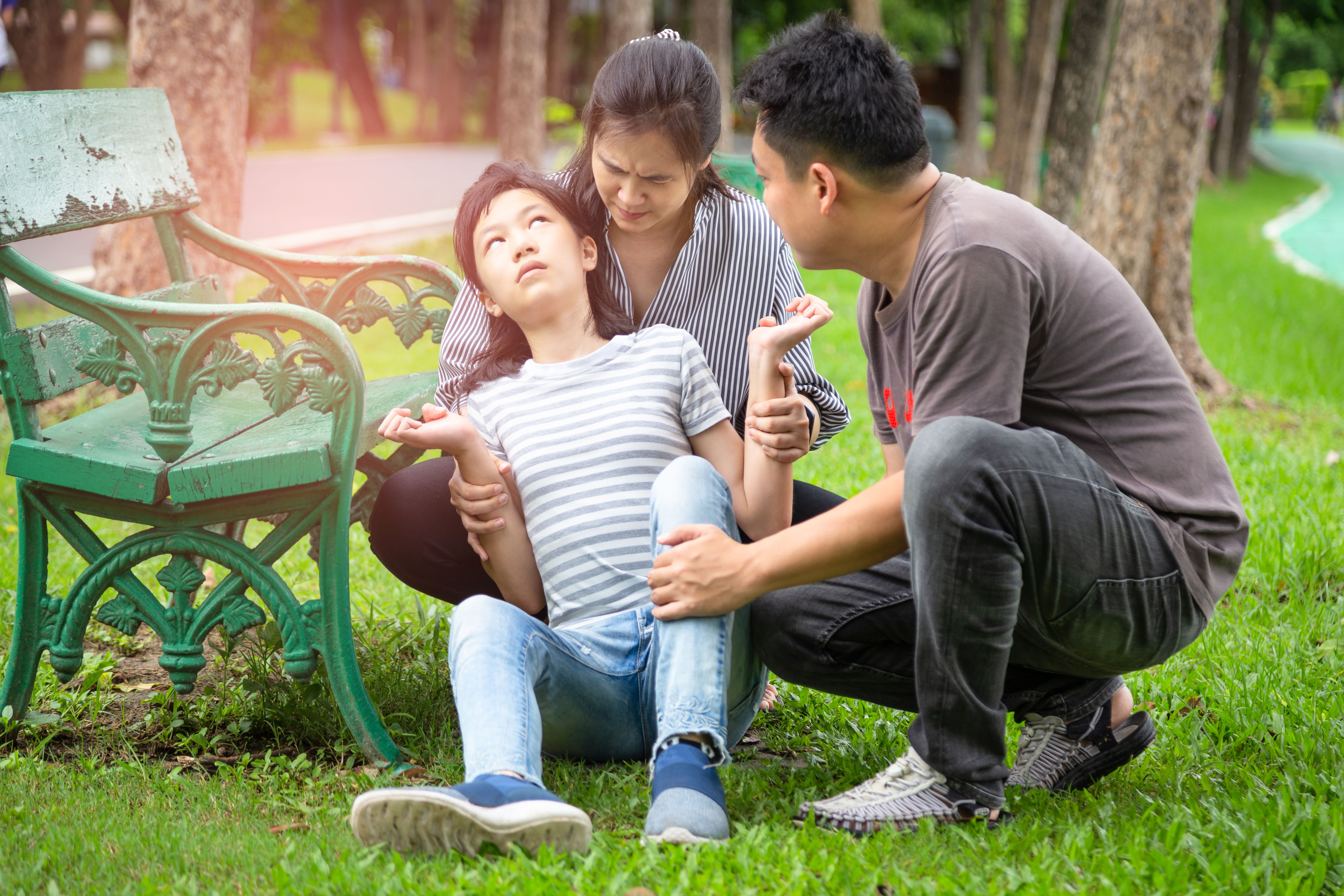
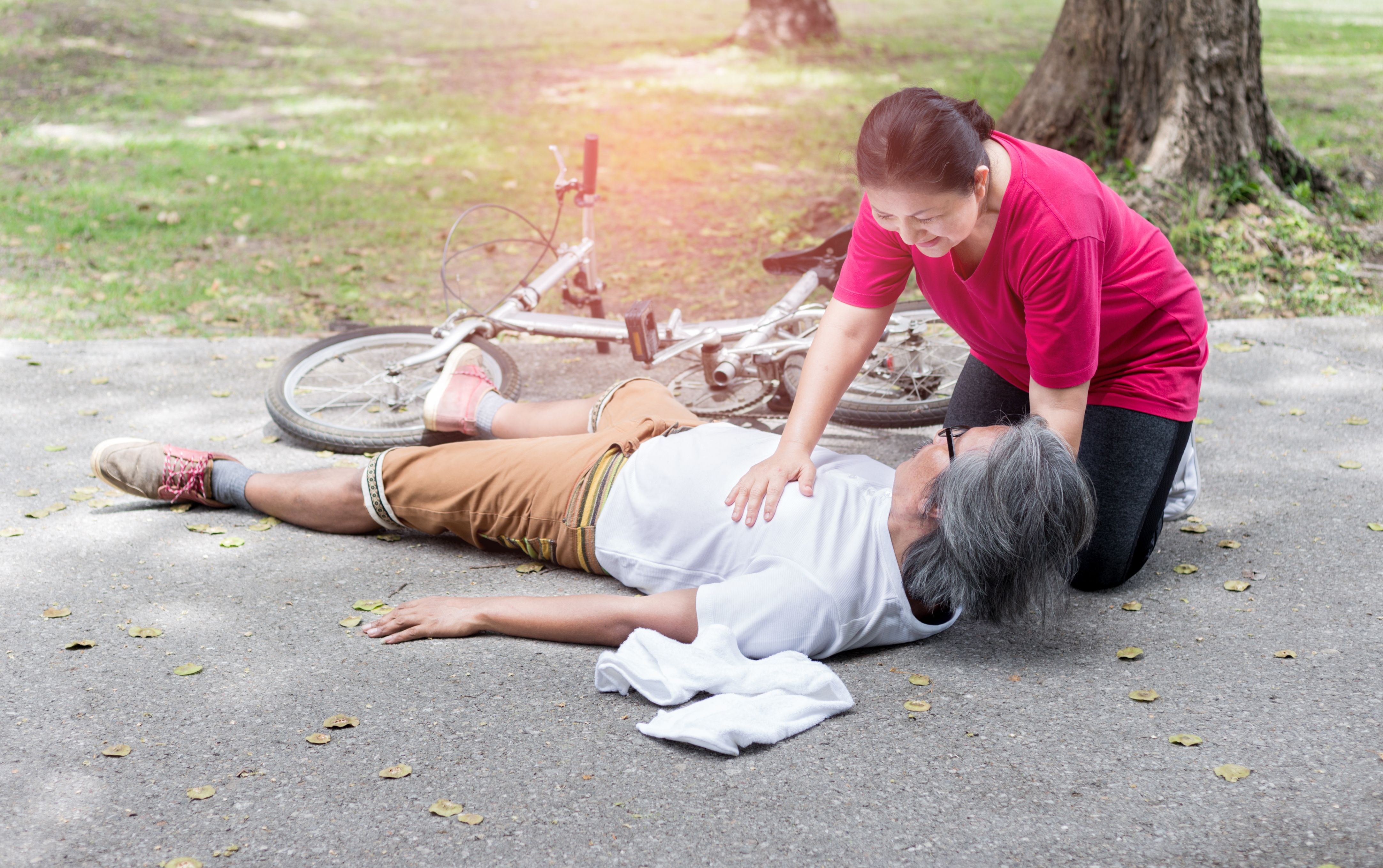
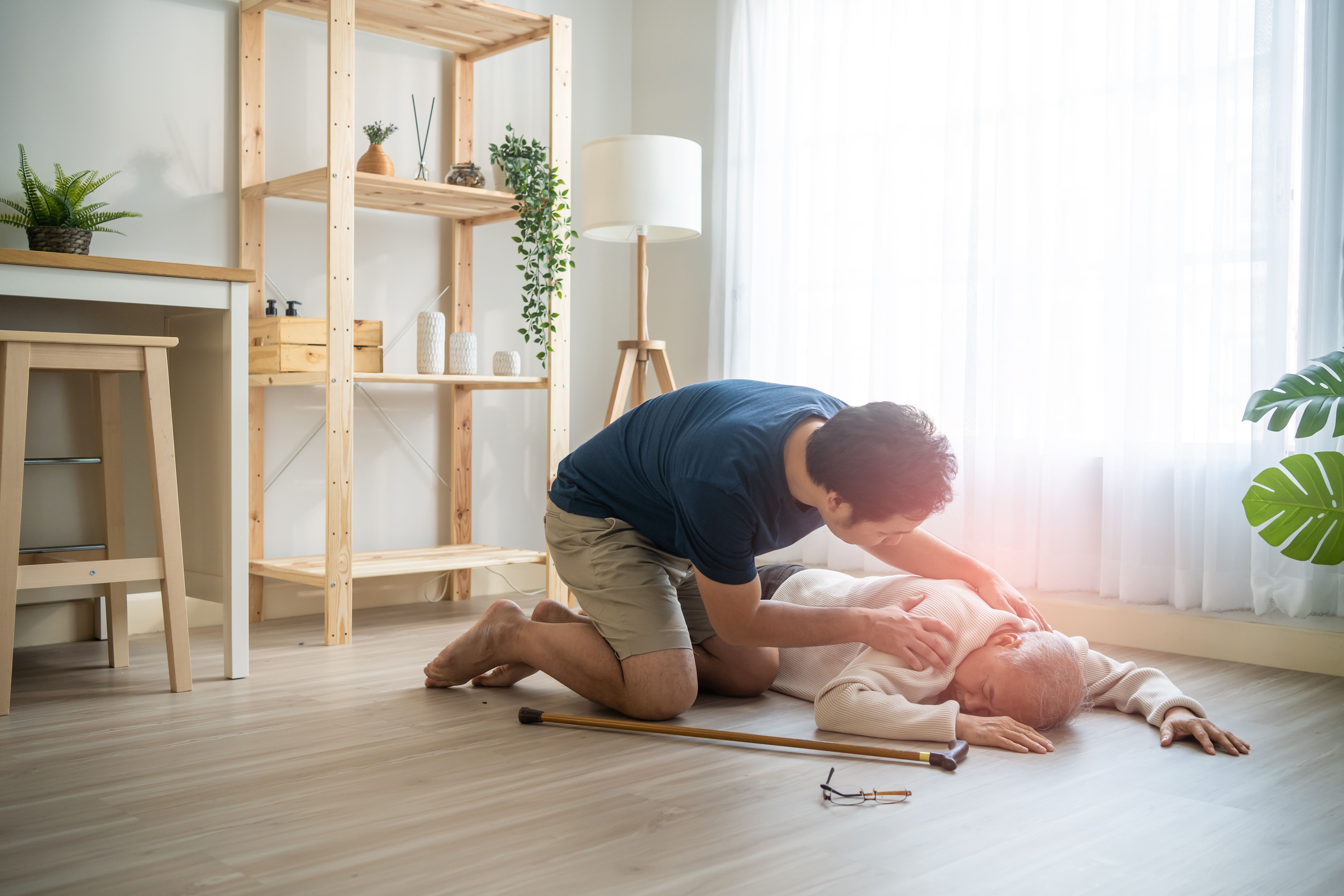
First aid for someone suffering an allergic reaction
- Ensure your own safety by assessing the environment around
- Remove the person from the area if the suspected allergen is in the environment.
- Assist with medication such as anti-histamines. As the name suggests, anti-histamines block the functioning of histamines which are chemicals released by the body due to allergens . If the medication is not on the person, you may be able to find it in a first aid kit
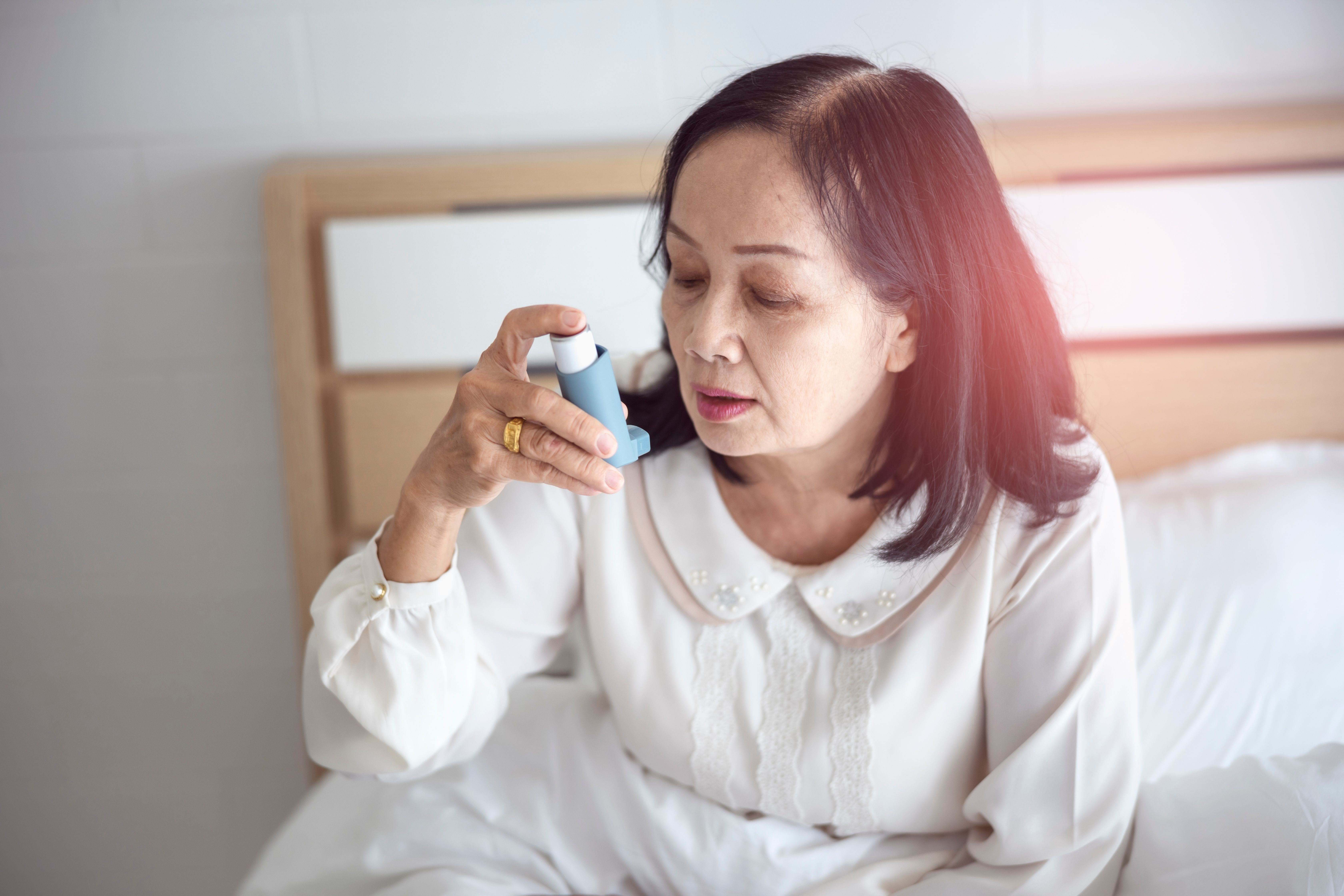
- If the person has a history of allergies or asthma, they may have a Salbutamol/Ventolin inhaler on their person, which can help open their airways.
- Assist with administration of the drug epinephrine using an auto-injectable device called an EpiPen. Epinephrines work by constricting blood vessels, which leads to increased blood pressure and decreased swelling.
- Call 995 for immediate medical help.
Long-term management of an allergy
The best way to manage allergies is to keep track of every substance a person is allergic to and keep those allergens away from their environment as much as possible. This may require checking the ingredients of food items to ensure that allergy-triggering ingredients are not in it. This may also require letting doctors know about any drug allergies a person may have. Medications such an antihistamines, Salbutamol inhalers and an EpiPen should be readily available if allergic reactions are serious. Consultation with an allergy specialist (Immunologist) and immunotherapy can also be considered With these efforts, allergies can be managed and kept to the level of a lifestyle nuisance rather than an imminent threat to life.
Article reviewed by Dr Kenneth Koh Eu Min, Medical Director and Co-founder, OneCare Medical