How to deal with respiratory problems
- CareBuddy
- 4 Mins Read
- 28 Jul 2022
- Common Health Issues

In various situations, we loosely say we cannot live without something. But it’s literally true in the case of breathing. We truly cannot live without it.
That’s why it’s imperative to understand respiratory problems and know how to care for someone suffering from one.
What is normal breathing?
Breathing is usually a quiet, effortless process. The air we inhale contains 21% oxygen. Our lungs retain some of this and we exhale air that’s 16% oxygen. The oxygen in our lungs is then transported by our blood to every cell in our body and that’s what keeps us alive.
A healthy breathing, or respiratory rate for an adult is 12 to 20 breaths a minute. For babies and children, it’s 20 to 30 breaths a minute. Respiratory rates above or below this can mean a disruption in the normal breathing process.
An easy way to measure breathing rates is to look at the rise and fall of the chest. Each rise corresponds to an inhalation and each fall corresponds to an exhalation. Together, they constitute one breath. The total number of breaths in a minute is the respiratory rate.
In case time is of the essence and you cannot wait 60 seconds to measure breathing rate per minute, you could count the number of breaths in 30 seconds and multiply by 2, or the number of breaths in 15 seconds and multiply by 4.
Common Respiratory Problems
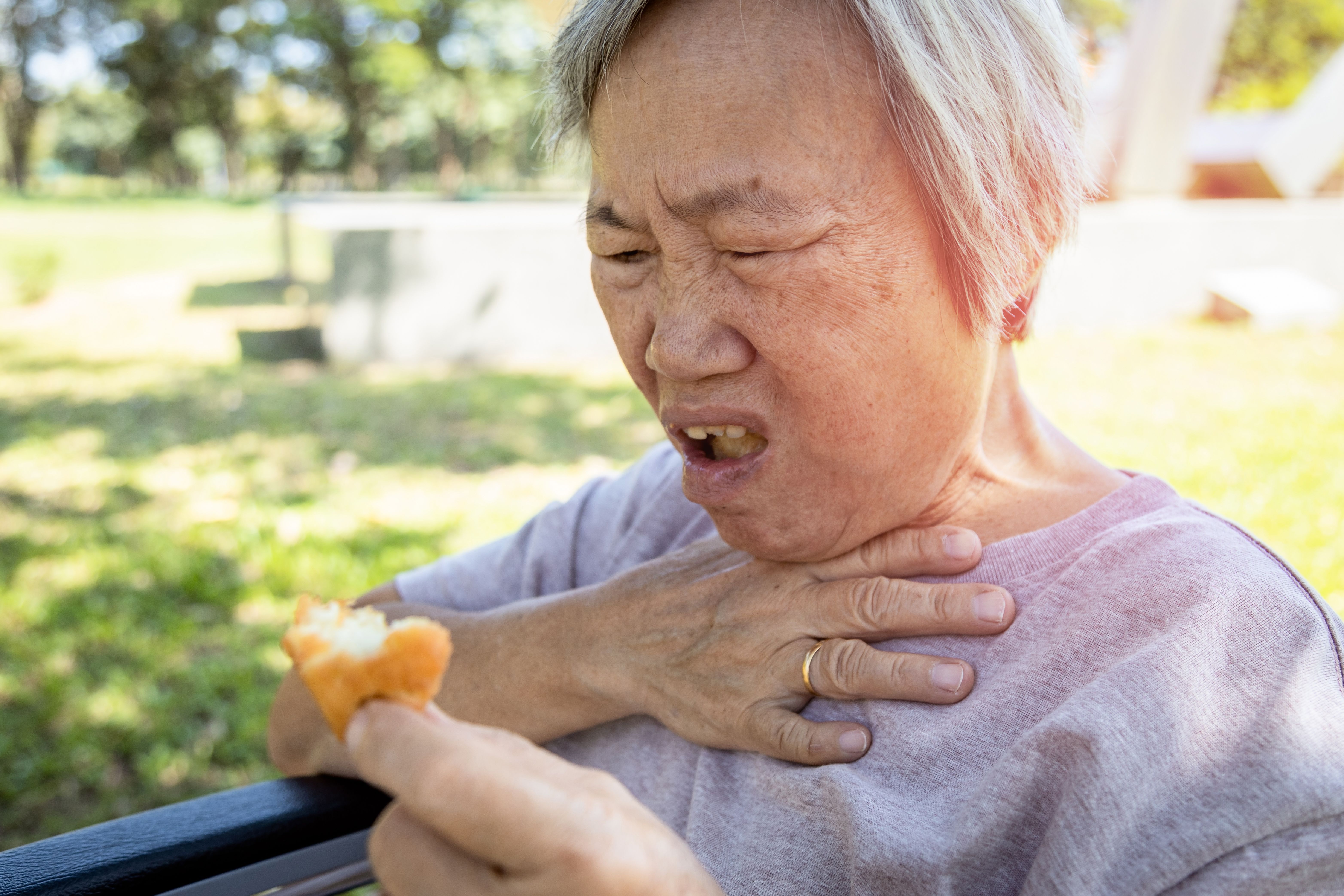
Choking / Foreign Body Airway Obstruction
A foreign body such as a piece of food can obstruct the airway and impede the breathing process either partially or completely.
If it’s partial choking, you can encourage the person to cough out the foreign body. If the choking is complete but the person is conscious, provide abdominal thrusts (or chest thrusts if the person is pregnant or obese) until the object is expelled or the person becomes unconscious.
If the person has become unconscious, follow the CAB sequence:
- Chest Compressions: Perform a set of 30 chest compressions
- Airway: Check the mouth to see if the object is seen, and remove it if it’s seen
- Breathing: Check breathing, and if there’s none, repeat the CAB sequence. You should also attempt two ventilations mouth-to-mouth or with a mask if available, for every 30 chest compressions, checking each time if there is resistance to airflow and if any foreign body has been dislodged.
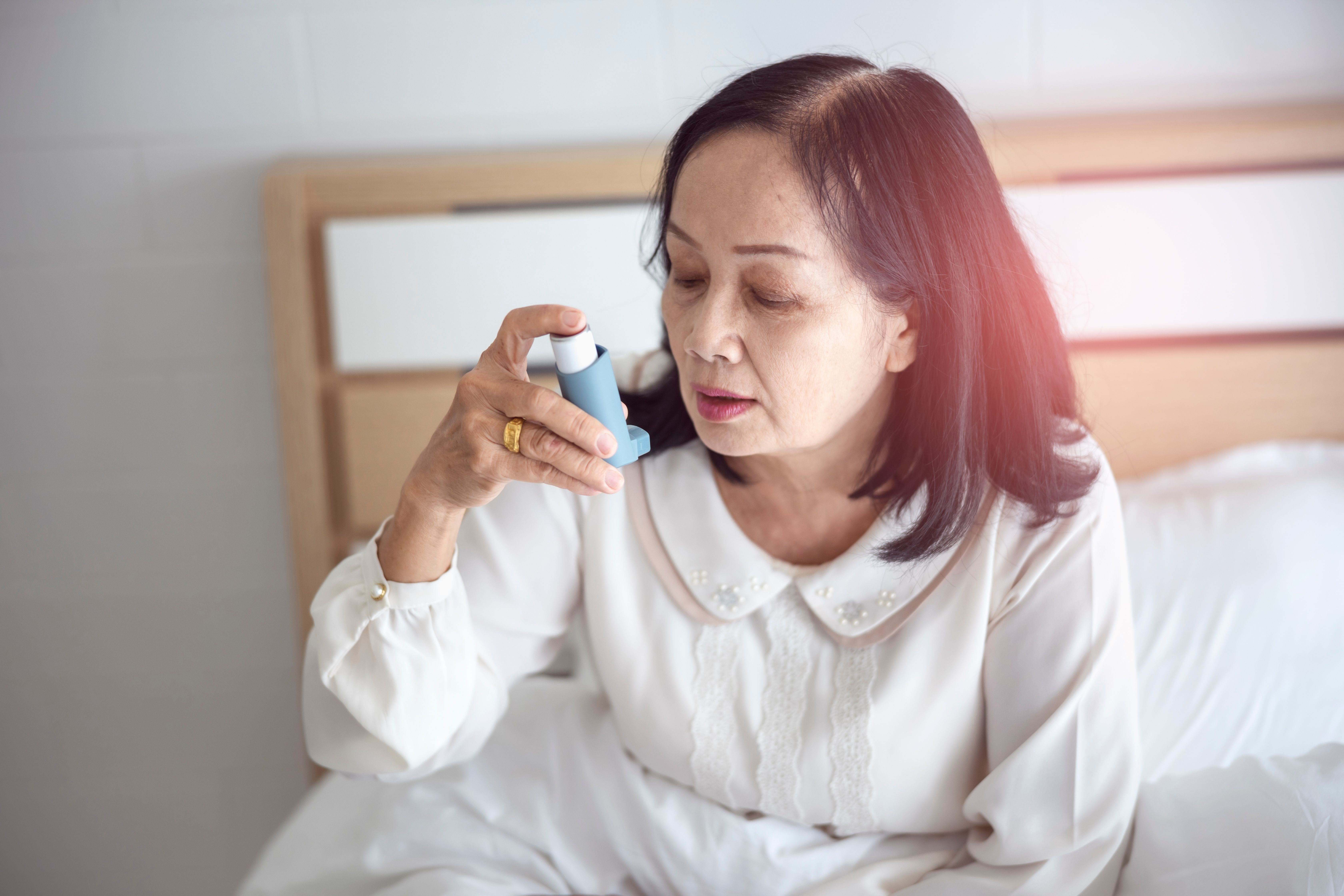
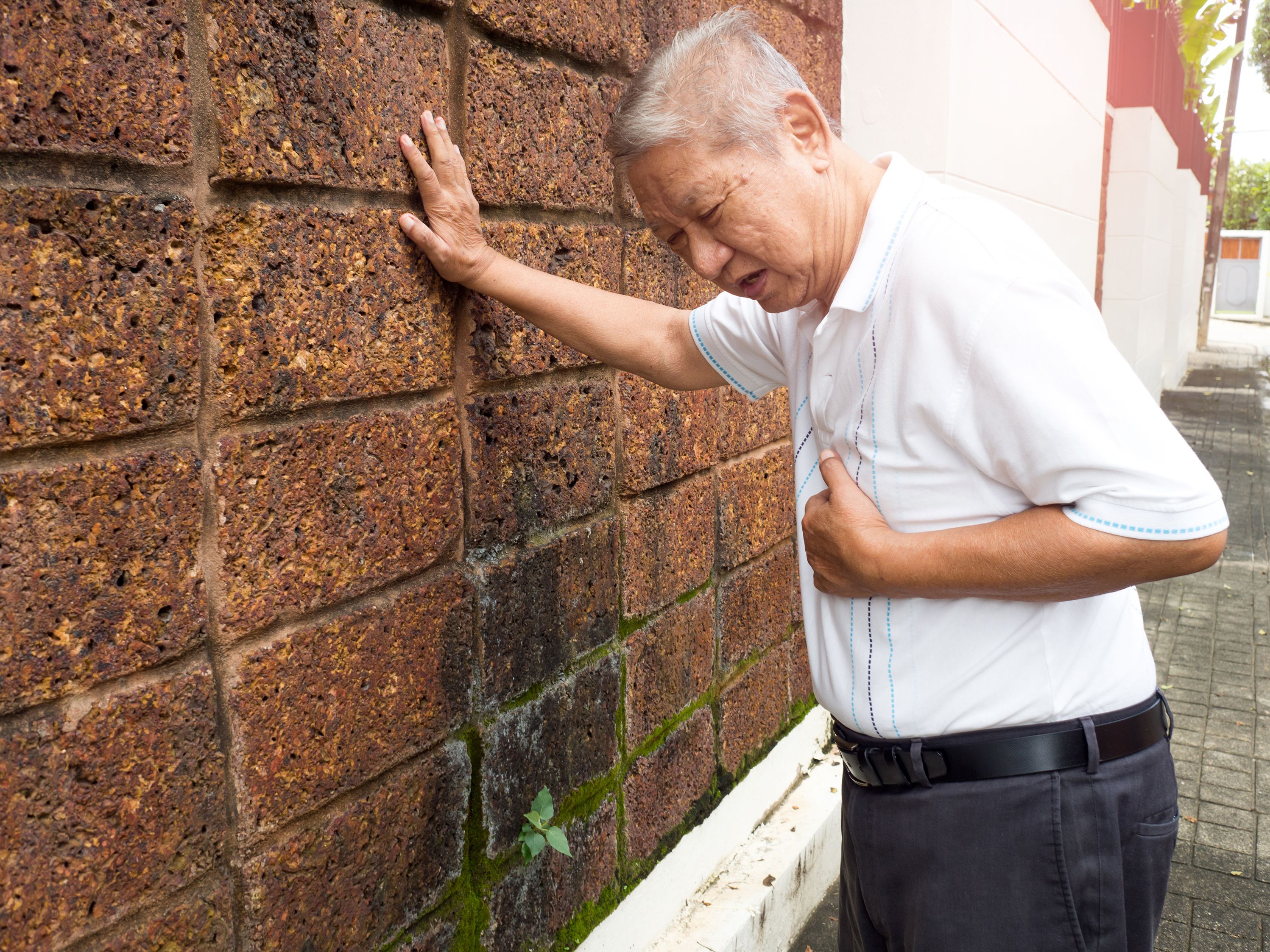
Asthma
Asthma is a condition in which airways narrow or swell and may produce extra mucus. This can cause breathing difficulties.
Symptoms include
- Breathlessness (struggling for air)
- Severe coughing
- Wheezing
- Pursed lips
- Flaring of nostrils
- Distress and anxiety
The steps of providing first aid to a person suffering an asthma attack are
- Place the person in a sitting-up position
- Tell them to breathe slowly and deeply
- Help them inhale a Salbutamol/Ventolin puff (which they may carry with them if they have frequent asthma attacks)
- Seek professional medical help if breathlessness persists
Hyperventilation
Stress or anxiety can make someone breathe rapidly. This is called hyperventilation. A little counter-intuitively, this overbreathing can actually lead to someone feeling breathless.
Symptoms include
- Fast, deep breathing
- Breathlessness
- Panicky, hysterical demeanour Dizziness, faintness
- Dizziness, faintness
- Trembling or tingling of the extremitiesof the hands and feet, or of the lips
- Clawing/spasm of fingers/feet
To provide immediate care to someone experiencing hyperventilation,
- Speak to the person in a calm and reassuring way
- Ask them to breathe in and out slowly
- Watch out for non-respiratory symptoms that could suggest a more serious condition (e.g. cardiac arrest)
Fumes Inhalation
Fumes from chemicals can be a silent killer. A common source of deadly fumes inhalation is carbon monoxide that can come from
- Automobiles
- Portable stoves
- Lanterns
- Heaters
The reason this can be deadly is that carbon monoxide combines with hemoglobin in the red blood cells and reduces its oxygen-carrying capacity.
This can lead to symptoms such as
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Breathlessness
- Collapse
- Loss of consciousness
To provide first aid,
1. Wear personal protective equipment if available
2. Turn off the carbon monoxide source if possible
3. Move the affected person to an open area with fresh air
4. Sit or lay the person on their side, not their back
5. Maintain their airway
6. Perform hands-only CPR in case of respiratory arrest.
7. Call 995 and prepare for evacuation
Allergic Reactions
A lot of people have allergies to a variety of substances in their food (e.g. peanuts, shellfish, eggs, wheat), in the environment (e.g. pollen, dust mites, mould) or their medication. These allergies lead to a variety of symptoms including respiratory problems.
- Respiratory symptoms include
- Cough
- Pain while swallowing
- Hoarseness
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
Non-respiratory symptoms include
- Central Nervous System: Headache, anxiety, confusion and lightheadedness
- Skin: Pain, swelling, redness, flushing, itchiness and hives
- Gastrointestinal: Vomiting, diarrhea, cramping
- Cardiovascular: Low blood pressure, fast or slow heart rate
- Others: Watery eyes, loss of consciousness
To provide first aid,
- Remove the person from the area if the suspected allergen is in the environment.
- Assist with medication such as anti-histamines.
- Assist with administration of the drug epinephrine using an EpiPen device if available.
- Call 995 for immediate medical help.
Article reviewed by Dr Kenneth Koh Eu Min, Medical Director and Co-founder, OneCare Medical